To Drive a Manual Car
Half a century ago, people began to use a new, quite different way of driving. Yes, it was automatic transmission… Since then, a lot of people only know how to drive a car with automatic transmission. The following article was written for those who are learning to drive for the first time or to make it easier for people who drive vehicles with automatic transmission to switch to manual driving. We will discuss how to drive a manual car.
In today’s dynamic world, knowing how to drive is definitely not a luxury; It is a basic skill that enables people to enjoy life. It doesn’t matter whether people drive to work, go shopping, or travel to a national park to relax; Being able to drive provides more opportunities. The reasons are quite simple:
- Mobility and Independence: Ability to go wherever you need. With a car, you can drive wherever you want. Public transport is not always able to provide this level of flexibility. Indeed, apart from a vehicle, you will not think about the schedule and location of bus stops or the availability of a taxi in remote areas. This is especially important for those who live in areas with meager and infrequent public transport.
- Career Opportunities: There are many professions in which either having a driver’s license is an essential condition, or the applicant who has a certificate of the ability to drive a car will significantly increase their chances among competitors. These include sales representatives, truckers and other specialists delivering goods, as well as Lesotho police officers and ambulance drivers. Indeed, in some situations, knowing how to handle a vehicle can be important not only for the safety and convenience of the future employee but also depend on the health and lives of other people.
- Emergency Situations: Since drivers can always sit behind the wheel in case of an emergency or a sudden event, those who know how to drive do not depend on their slow legs, or they need to catch the last bus. It is also worth noting the ability of drivers to leave the danger zones, if there is information about a natural disaster, a stolen child, and other high-risk events. At the same time, traveling through empty and unsafe streets, or through wooded areas and rural spaces, alone or with other people, will also be safe.
- Flexibility and Convenience: An excellent way to relax at the weekend with friends is the idea of riding a bike to a picnic spot. The availability of a bike rack tightened on the trunk of a car reduces the time of movement and fatigue during a picnic. That is why riding a bike, a roller, or traveling on foot is not always convenient and practical.
Car Transmission Types
Now, before moving on to the topic of driving a manual car, let’s examine the difference between automatic and manual transmission cars.:
● Automatic Transmission:
An automatic transmission its car that the gears change by themselves as the car goes quicker or slower. As we can see when the car is too slow and pause the car gets reverse without manual change of that into reverse negotiates forward. The car will change automatically into the parking point the driver does not have to get out the car to do that his or her self. It is also easy to drive the car in a traffic city place or city town. These types of car the driver will only have to select the car modes e.g. drive (D), reverse(R), neutral (N), and parking (P). It’s useful for heavy traffic or in the upward hill places.
● Manual Transmission:
Manual transmissions car require the driver to change the car gears by he or herself using the gear stick and the clutch pedals e.g. “standard” or “stick shift. These cars have more advantages though it a bit difficult for learner’s and for lazy drivers then there wouldn’t be a gearbox. They have the pace that can not be used by an automatic gymnastic. They are cheaper to buy than the automatic cars also they are saleable. They perform better especially when the engine needs lots of power.
Learning to Drive A Manual Car
Driving a manual car is more than just a mechanical skill to master; it’s a way of forming a profound connection with the car and the road. In a world where automatic transmissions are conquering the markets, learning to guide a manual car gauges a unique experience. You study something that is not simply a way of moving around but a rewarding pursuit.
However, the art of manual driving is not just for adherents and those devoted to the subject. Indeed, it’s a useful skill for every driver on the road. Whether you’re starting your journey with cars or are already an automatic car owner, manual transmission can be beneficial to learn. It might mean that you’re already aware of how to drive, but manual driving opens you up to many new things and makes you a more comprehensive driver.
There are numerous advantages related to driving a manual car that pertain to something beyond mechanical. It provides a sense of control that regular drivers will never understand: manual cars make you much more engaged in the process of driving. They’re more fuel-efficient, and better performing in many cases, which gives you a little ego boost when the automatic cars are struggling with a steep hill. In addition, manuals are more reliable and require less maintenance.
This study is aimed at two main groups:
1- Beginners who want to learn how to drive a manual vehicle
2- Automatic vehicle drivers who want to switch to manual driving.
If youare in one of these groups, you are inthe right place. Mastering a manual transmission is not an impossible goal. It’s easy to do with the right practice and understanding. Thus, we can start with a brush-up session to review all the needed information. That’s the simplest way to understand how to learn to drive a manual.
1. Understanding the Basics of Manual Transmission to Drive a Manual Car
Before learning how to drive a manual car, be in a position to understand the basics of how the transmission system works. Therefore, in manual cars unlike automatic cars which do the job themselves, in manual cars, you do the changing of gears. You are supposed to shift the gears up to accelerate, down to decelerate, and neutral to idle or maintain speed. Moving the stick shifts the gear. Several components form the basis of the transmission system for a manual car:
● Components of Manual Transmission:
At the heart of a manual transmission system are several key components:
- Clutch: The clutch is on your car’s left, adjacent to the brake pedal, that is, at the center of the two pedals. It helps to separate or disengage the vehicle’s engine from the gearbox. Therefore, as a driver changes to an optimal gear, the clutch provides a smooth transfer and setting in motion the gear between the wheel, chassis, and engine.
- Gearbox: Gearbox, also known as Transmission: Encase the gears of the car that help in distributing power from the car engine to the wheels. The modern manual car has various numbers of gears occasionally up to 6. Gears have varying ratios to suit different driving conditions.
- Gear Shift Pattern: Manual cars have a long lever on the center console extending up to the height of the steering wheel. Some cars have a mechanism for the gear stick to be located directly at the steering wheel. The manual cars follow the transmission of gears that a different manual car makes: the first gear, second gear, third gear, fourth gear, fifth gear, and reverse.
● Coordination Between Clutch, Gear Shift, and Accelerator:
The most fundamental part of starting the engine of a manual car is learning the coordination between the clutch and the accelerator. This leads to the importance of the smooth operation of gear transitions.
To establish motion, in a straight and level ground forward, the driver engages the clutch and on first gear whilst stepping slightly on the accelerator. Since the engine is in constant downturn, as the clutch is released, the engine starts rotating the wheel. Upon attaining a speed of 5 mph to 10 mph the driver engages the clutch and on second gear then releases the clutch slightly whilst pressing the accelerator to pick up speed. Finally, the clutch is engaged and the third gear is switched. The smooth release of the clutch, and clutch engagement, leads to the correct acceleration.
The combination of the basic understanding of the clutch, gear shift, and accelerator part in enhancing the performance of a manual car. Over the course of time and adequate practice, the transition of the gear shift will become natural.

2. Getting Comfortable in the Driver’s Seat
Before getting into the nuances of manual driving, it is important to ensure that one is well situated behind the wheel. The most comfortable position behind a wheel increases control and minimizes fatigue during long drives.
● Adjusting the Seating Position:
- Seat Height: One should adjust the seat height. When one play with the height settings they should be able to get a clear view of the road and of the car’s controls as well as easy access to car’s pedals.
- Distance from Pedals: One should adjust the seat relative to the pedals. The idea is to place one’s body so that while depressing the pedal all the way one needs to have a slight bend in the knees. This body positioning will help one drive the car comfortably.
- Seat Angle: Adjust the angle of the seatback. Setting the seatback to comfortably support one’s back maintaining a slight backward tilt will put one’s hands at the correct distance and angle to the steering wheel and car’s controls.
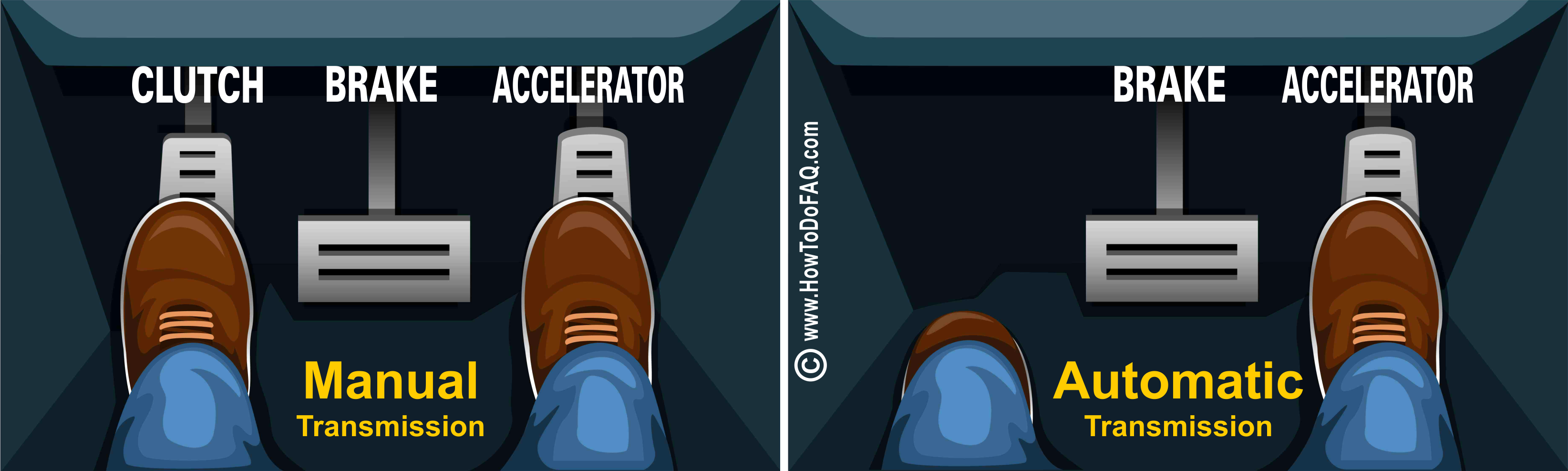
● Familiarizing with the Pedals to Drive a Manual Car:
The pedal on the left is the clutch pedal. The middle, or the second pedal is the brake pedal. The pedal on the far right is the accelerator. One could use the mnemonic *C-B-A,* for clutch, brake, and accelerator, which racks up respectively with the left to right positioning of the pedals. The positions work both for the right-hand drive and the left-hand drive cars.
- Clutch: Always press the clutch smoothly and at a consistent speed to disengage the engine from the gearbox. By doing so, you will train yourself to be in tune with the sensitivity of the pedals and the way they resist against your pressure. This way, you can ensure smooth gear changes.
- Brake: It is very important to get a sense of the brake pedal’s feel and travel distance to train your foot accordingly. For normal braking, do it gradually and smoothly. But when it is an emergency, use your foot to step firmly and quickly to stop the car.
- Accelerator: Doing so helps you understand the sensitivity of the gas pedal and the required foot positions. Make it a point to keep your foot in a position from which you can easily modulate the car’s acceleration.
● Practicing Clutch Control: Finding the Biting Point:
- Biting Point: The biting point results from the position at which the clutch begins to engage and propel power from the engine to the gearbox. Method:
- Make use of your left foot to press the clutch pedal down completely.
- Shift the gear lever to the first gear.
- Gradually release the clutch pedal until you feel some resistance or until the car may start moving to the front slightly.
- That specific position is the biting point instance when the clutch begins to engage.
- Smooth Transitions: It will assist in making smoother shifts and avert the car’s stalling.
- Hill Starts: Such a practical exercise is vital in mastering this skill, especially when one has to drive uphill. In that case, the pressing of the clutch, acceleration, and braking have to be well-coordinated to avoid counter-drifting.
3. Starting and Stopping Smoothly When Beginning to Drive a Manual Car :
Starting and stopping smoothly are essential skills of manual driving , ensuring a comfortable and safe driving experience for you and your passengers ..
● Step-by-Step Guide to Starting the Car in First Gear :
- Preparation : Ensure the hand-brake is engaged, and the gear lever is in neutral .
- Starting the Engine : Depress the clutch pedal,and start the engine using the ignition key or button.
- Selecting First Gear : With the clutch pedal still depressed, shift the gear lever into first gear .
- Finding the Biting Point : Gradually release the clutch pedal until you feel the biting point , where the car begins to move forward slightly.
- Smooth Acceleration : While maintaining slight pressure on the accelerator pedal, continue to release the clutch pedal smoothly until it’s fully engaged .
- Adjusting Acceleration : Modulate the accelerator pedal to control the speed of the car, gradually increasing speed as you gain confidence .
● Method s of Smooth Acceleration and Gear Shifting :
- Rev-Matching : Matching the speed of the engine to the speed of the targeted gear while downshifting or upshifting can help to avoid jerks and minimize the wear on the clutch and transmission n.
- Progressive Acceleration : Also it is essential not to make any rapid movements with the accelerator pedal . It is much better to have steady and gradual acceleration. It will contribute to making the driving experience stable.
- Timing of Gear Changes: It is vital to understand when it is all important to shift gears. It can be done, for example, on the condition of slowing down and stopping, increasing the speed, or other circumstances related to the driving conditions, traffic on the road, or speed limitations.
● Know How to Slow Down and Stop with Engine Braking and Downshifting:
- Engine Braking: Engine conditions while losing speed, and downshifting down one gear cause Engine Braking to slow down the vehicle. It works well for going downhill, helps not to use the brakes inside the rotor, and saves up more energy for boots.
- Downshifting Technique: downshifting to lower gear is considered the proper technique, so here is how to do it in an accurate and effective way:
- Depress the clutch pedal, keep it like that, grab a lower gear, and leave the gas lever for now.
- Rev-match is when you rev the lever throttle, which means accelerate so speed will be closer after new lower gear enters.
- Release the clutch pedal while pushing the accelerator smoothly to make the entire process safe for your transmission.
4. Mastering Gear Shifting
Gear Shifting is one of the most basic yet essential elements of manual driving, defining the speed, efficiency and performance of the car. Knowing and understanding gear ratios and when to shift gears will help both extend your driving life and make the driving experience more enjoyable.
● Detailed Explanation of Gear Ratios and When to Shift Gears:
- Gear Ratios: Each gear inthe transmission system has a specific gearratio. It defines the relationship betwen that gear’s engine speed, or RPM, and the wheel speed, or rotational speed of the wheels. Lower gears provide a higher torque for acceleration while the higher gears allow for better fuel economy and a car frame at top speeds.
- Shifting Points: Knowing when to shift your gear depends on the engine speed, car speed and the type of terrain you may be driving on. In general, gear shifting is done at higher RPMs when upshifting and lower RPM when downshifting, when the engine speed slows down and runs at an RPM that cannot produce full power or performance.
● Practice Exercises for Upshifting and Downshifting Smoothly:
- Upshifting: The first exercise can be done by paying close attention to your engine RPM and time. Find the appropriate time to switch up through your gears and start accelerating. Do this more from first gear up to your last. Another exercise is to try downshifting first to a smaller gear and even shifting up. Do this faster and try accelerating at the same time. For example, downshift from the 6 th gear to 3 rd or 4 th gear, the gear will go up
- Downshifting: Downshifts can be mainly on to the last one or the first one. You can do this smoothly without causing any instability. When slowing down at the bottom shift, let the next gear has charges so to can perfectly shift back easily.
● Tips for Anticipating Gear Changes Based on Speed and Road Conditions:
- Speed Awareness: Check your SPL tracker Relationship. Always look ahead and plan for the anticipated move. Frequent readings of the gauge might cause mistakes. As soon you see or realize you undoing the wrong move take some slight action and adjust things to go back to the first plan.
- Road Conditions: the other action is downshifting when driving down a hill. It provides the engine will not have to support the overall speed power thus the driver easily downshifts. It is essential to have the finger on the up/downshift monitors to avoid making mistakes in moving back to the first gear. Other spectators might be the roughness or smoothness of the road. The curving of the large or mild road can be crucial to considering how you start reducing the speed. In summary when on a road slope always try to downshift.
5. Navigating Challenging Situations
Driving a manual car may be difficult in some situations because you regularly need to come up with some specific maneuvers and strategies to keep you safe and follow the route.
● Handling Hills: Uphill Starts and Downhill Descents:
- Uphill Starts : Uphill starts require the use of a handbrake ,to avoid rolling backward . Thus, the driver needs to depress both the clutch and the brake, find the biting point of the clutch, and shift into the first gear . After that, it is necessary to put some accelerative pressure on the gas pedal, hold the clutch until the proper multitasking level is achieved, and release the handbrake.
- Downhill Descents: Driving downhill is all about using the engine and keeping the gear low to maintain speed as you descend. However, it is important not to press the brakes too hard because this is bad for the vehicle.
● Dealing with Traffic Jams and Stop-and-Go Situations:
- Clutch Control: The ability to control the clutch makes a driver’s life easier when stuck in traffic. This enables the driver to crawl well without the need of shifting down every time you stop. In addition, the car should try and keep a decent gap from the car in front as they’ll be able to anticipate any sudden traffic stops.
- Crawling in Gear: Stop-Starting in traffic not only tends to brake some cars but creates significant wear and tear in the vehicle’s clutch. So instead of constantly moving off in first gear and then setting the car in neutral, it’s best to keep the car in first gear, but run-in at low-low revs. The driver should be able to move the vehicle smoothly by continuously popping and then releasing the clutch while sneezing a little bit.
● Tips for Parking and Reversing in a Manual Car:
- Hill Parking: Activate the handbrake and leave the vehicle in gear, it may be either first or reverse gear. To prevent the car from rolling downhill, the front wheel s must be turned away from the curb.
- Reverse Gear: In an open space, practice reversing to become confident about how the clutch works in reverse. The use of side mirrors and rearview cameras may also assist you in staying control in tight places.
■++



